What Is DNS Encryption and How Does It Work?
Learn how you can encrypt your DNS traffic to improve privacy and prevent cyber attacks.
Imagine if someone tracked your every movement in real life, knowing exactly where you’ve been, how long you've been there, and how often you’ve visited that place. That would be pretty scary, right?
Well, that’s exactly what happens to your web traffic; each and every website you visit can be traced back to you. To make matters worse, this information can be used against you to conduct one of many cyberattacks, which can have severe consequences for you or your organization.
Luckily, a solution to this problem exists – Domain Name System (DNS) encryption. DNS encryption can help prevent malicious actors from snooping on and manipulating your DNS data for their benefit.
This article will explain what DNS encryption is, why it’s important, and what measures you can take to ensure your DNS data is safe from prying eyes.
What is DNS encryption?
DNS encryption is the process of securing DNS queries and responses from outside interference, ensuring they stay private, confidential, and free from cyberattacks. This is done through various techniques, such as DNS over HTTPS (DoH), DNS over TLS (DoT), and DNSCrypt.
Encrypting your DNS traffic is crucial to your overall DNS security since it addresses vulnerabilities in the DNS protocol. But how does it all work?
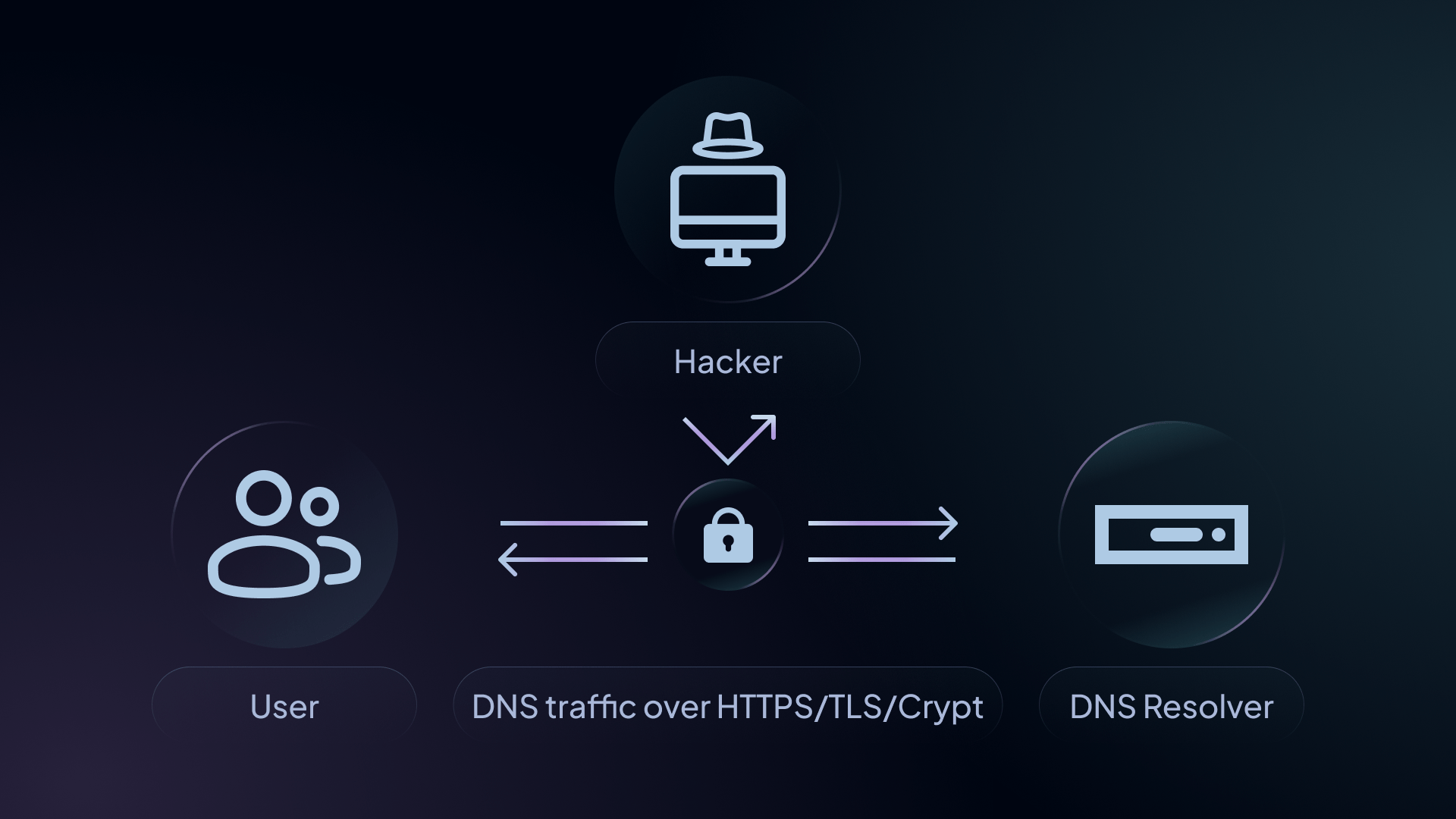
How does DNS encryption work?
DNS encryption works by scrambling plaintext DNS data into an encrypted message that can only be deciphered by the DNS client (i.e., your device, browser, or network) and the DNS resolver.
There are several key steps to the DNS encryption process:
- Client configuration: You must first configure your device or network to use encrypted DNS resolvers. This usually involves specifying the resolver’s IP address, port, and encryption protocol (more on this later).
- Selecting a resolver: Encrypted DNS resolvers serve as the middleman between clients and authoritative DNS servers. They are responsible for encrypting DNS queries, forwarding them to authoritative servers, and decrypting the responses back to the client. The best customizable DNS resolvers will configure your device for you and offer a variety of additional features such as AI malware blocking, DNS filtering, and more.
- Encryption: Now that DNS encryption is set up, all DNS queries between clients and authoritative servers will be transmitted through an encrypted ‘tunnel’, keeping it confidential and unreadable. Any outside party attempting to read your DNS traffic will see random characters that don’t make sense.
Why encrypt DNS traffic?
Encrypted DNS traffic means that no third parties can view or change your DNS queries and responses – whether that’s a malicious attacker, your Internet Service Provider (ISP), or anyone else. This ensures that your DNS requests and responses remain private without manipulation.
Unencrypted DNS traffic is transmitted in plaintext, which means it is readable by anyone who has access to your DNS data. This presents opportunities for malicious actors to engage in packet interception, transaction ID to query matching, and data modification.
Therefore, it exposes you to cyberattacks such as DNS spoofing, DNS amplification, and DNS hijacking, to name a few. These attacks can lead to data theft, identity fraud, financial fraud, and more.
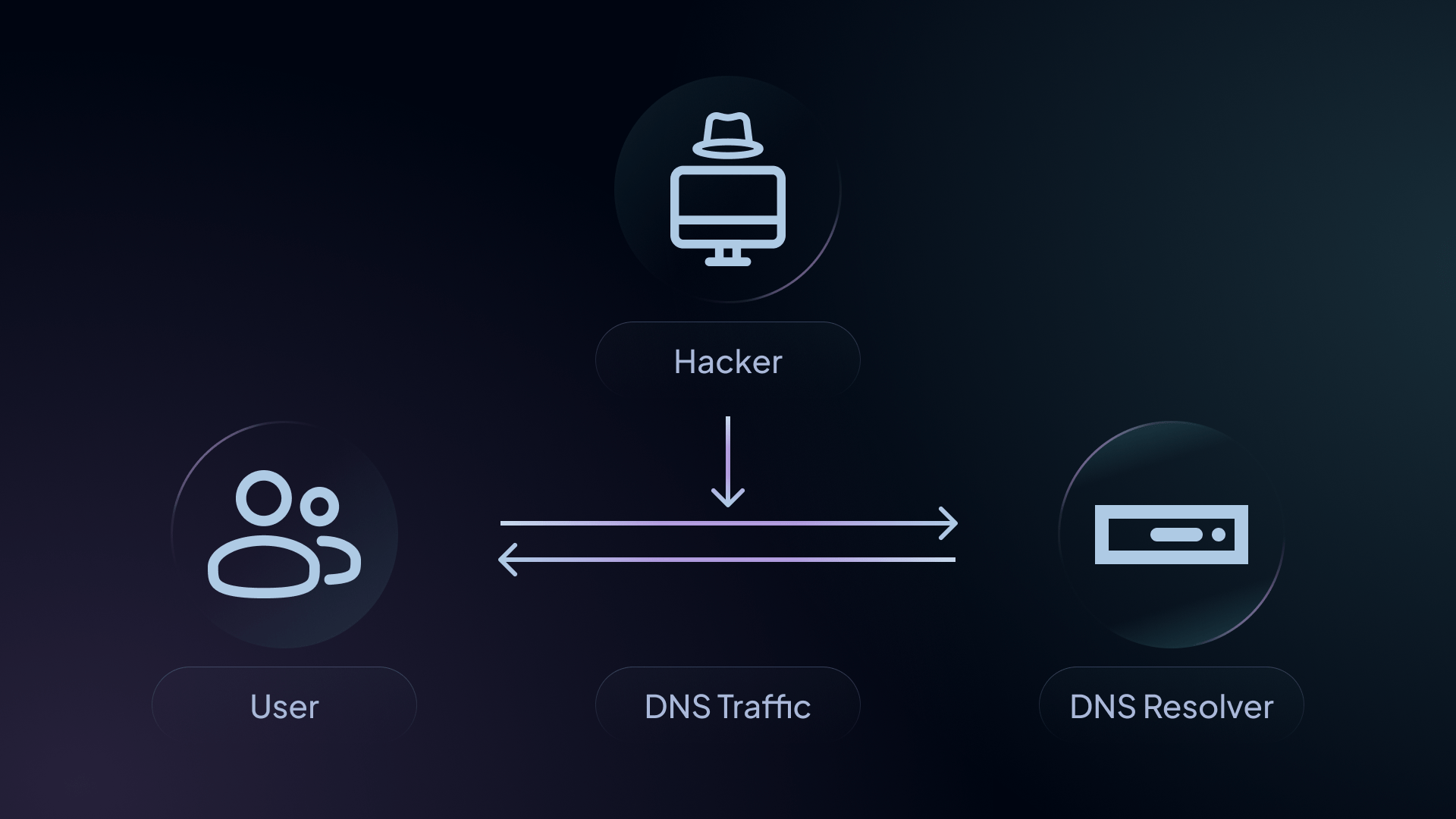
How to encrypt DNS traffic?
The three main methods to encrypt DNS traffic are DNS over HTTPS (DoH), DNS over TLS (DoT), and DNSCrypt. All three DNS encryption protocols offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that your DNS traffic remains confidential.
These methods can be challenging to implement for those who aren’t tech-savvy. Fortunately, an easy solution is to use a DNS resolver.
Customizable DNS resolvers allow you to encrypt your DNS data with a click of a button, doing all the heavy lifting for you.
But what are the differences between each encryption protocol? Let’s find out.
DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
DoH protocols encrypt DNS traffic using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) infrastructure. They operate in Layer 7 (Application Layer) of the OSI model and utilize Port 443, the same port used to send HTTPS requests.
As such, all DNS requests and queries are encrypted as if they were HTTPS web traffic, ensuring your DNS traffic remains confidential, private, and authenticated.
DNS over TLS (DoT)
As the name suggests, DoT encrypts DNS queries using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol in Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of the OSI model. Unlike DoH, which relies on the HTTPS infrastructure, a secure TLS connection is made between the client and the DNS resolver – typically via Port 853.
Many people prefer using DoT because it uses a completely new port solely for encrypted communication. This enables them to troubleshoot and easily identify any issues instead of sifting through HTTPS web traffic data. It also tends to have lower latency compared to its DoH counterpart.
DNSCrypt
DNSCrypt is a network protocol that masks all DNS traffic between clients and resolvers with cryptographic encryption. It also authenticates your DNS responses to ensure they came from the correct DNS resolver and haven’t been modified or altered in any way.
Instead of HTTPS or TLS, DNSCrypt encrypts data over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), utilizing Port 443.
What are the benefits of DNS encryption?
Encrypting DNS queries for both individual users and organizations has several benefits. These include:
Enhanced privacy
Encrypted DNS traffic prevents ISPs and malicious actors from monitoring and tracking your online activity. This lets you browse the internet with peace of mind, knowing nobody is snooping on your DNS queries.
Improved cybersecurity
DNS encryption blocks malicious actors from modifying or tampering with your DNS data, thus protecting you from cyber attacks such as DNS spoofing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and DNS hijacking. This is particularly prevalent for those operating on public WiFi networks.
Proactive measures
Prevention is better than a cure, and this also applies to DNS. DNS attacks – and all other cyber threats – are constantly evolving, and in such a fast-changing landscape, it’s essential to be proactive in your DNS security measures. Encrypting your DNS requests and responses will help you prevent attacks from occurring in the first place instead of trying to play catch-up after the damage is done.
What are the drawbacks of DNS encryption?
Performance and latency
Encrypted DNS traffic can introduce latency, especially if you encrypt your traffic via DoH. This is because you’re adding additional steps to the DNS resolution process. While the increased latency may be minor, it can be noticeable for some people. However, you can easily counteract these effects with a DNS resolver.
Your private DNS resolver will have DNS filtering capabilities to block ads, trackers, and more. These increase latency because they require additional data transfer between your device and the website through more HTTPS requests.
Since these requests are blocked from being resolved in the first place, web pages will load faster, and your overall performance may actually increase.
Bypassing Censorship
Some ISPs and governments may enforce censorship by blocking access to certain websites or services. While DNS encryption will encrypt your DNS queries, the Server Name Indication (SNI) TLS extension will still be communicated in plaintext.
Since this SNI information is not encrypted, those using Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) technologies can track which websites and services you visit, meaning DNS encryption will not provide any security benefits. For such use cases, it’s best to use a VPN.
Conclusion
DNS encryption is essential to your overall DNS security measures, regardless of which encryption protocol you use. Its proactive nature helps enhance privacy, improve cybersecurity, and, in many cases, improve browsing speed when used with a private, customizable DNS resolver.

